In our fast-paced world, risks evolve rapidly, requiring us to minimize their threats while maximizing their potential. Organizational risk represents the potential for losses due to uncertainty. A successful enterprise risk management program enables an organization to consider the full spectrum of risks and disruptions it faces, along with their impact on strategic goals.
Why is enterprise risk management important?
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) is a strategic approach that views risk management from the perspective of the entire organization. This top-down approach to managing risks aims to identify, assess, and prepare for potential threats, hazards, and other risks that could disrupt operations or impede the achievement of organizational objectives, potentially leading to losses.
An effective enterprise risk management method, if integrated properly, can result in substantial cost savings for the company. It helps control future outcomes as much as possible by acting proactively rather than reacting to situations as and when they arise. ERM helps minimize both the possibility of a risk occurring and its potential impact.
Key takeaways
-
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) is a comprehensive strategy designed to identify and prepare for risks affecting a company's finances, operations, and strategic objectives.
-
ERM enables managers to influence the company's overall risk profile by requiring specific business units to either engage in or refrain from certain activities.
-
Unlike traditional risk management, which tends to be siloed and department-specific, ERM promotes a holistic approach that considers the interdependencies between departments.
-
Effective ERM strategies can mitigate a wide range of risks, including operational, financial, security, compliance, legal, and more.
What are the 3 main types of enterprise risk?
The three main types of enterprise risk typically addressed in Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) are:
Operational risk: Risks arising from day-to-day business operations, such as system failures, process inefficiencies, or supply chain disruptions.
Financial risk: Risks related to the financial health of the organization, including market fluctuations, credit risk, liquidity issues, and investment losses.
Strategic risk: Risks that could affect the achievement of the organization’s strategic goals, such as changes in the competitive landscape, shifts in customer preferences, regulatory changes, or ineffective business strategies.
Other types of risks enterprise risk management addresses include:
- Compliance risks: Risks associated with failing to comply with laws, regulations, and industry standards, which can result in legal penalties and reputational damage.
- Security risks: Risks related to the protection of the organization’s assets, including cybersecurity threats, data breaches, and physical security breaches.
- Environmental risks: Risks stemming from environmental factors, such as natural disasters, climate change, and resource scarcity.
- Legal risks: Risks arising from legal actions or disputes, including lawsuits, intellectual property issues, and contractual obligations.
- Technological risks: Risks associated with technology, including system obsolescence, technological innovation, and IT infrastructure failures.
- Political Risks: Risks arising from political changes, such as regulatory shifts, government instability, and changes in trade policies.
Risk management strategy
The goal is not to eliminate risks altogether but to assess and manage risks and take calculated decisions that preserve and add to enterprise value. By implementing risk management techniques - risk avoidance, risk mitigation, risk transfer, and risk acceptance - an organization can discover which risks are worth taking. ERM follows a very distinct and ongoing process:
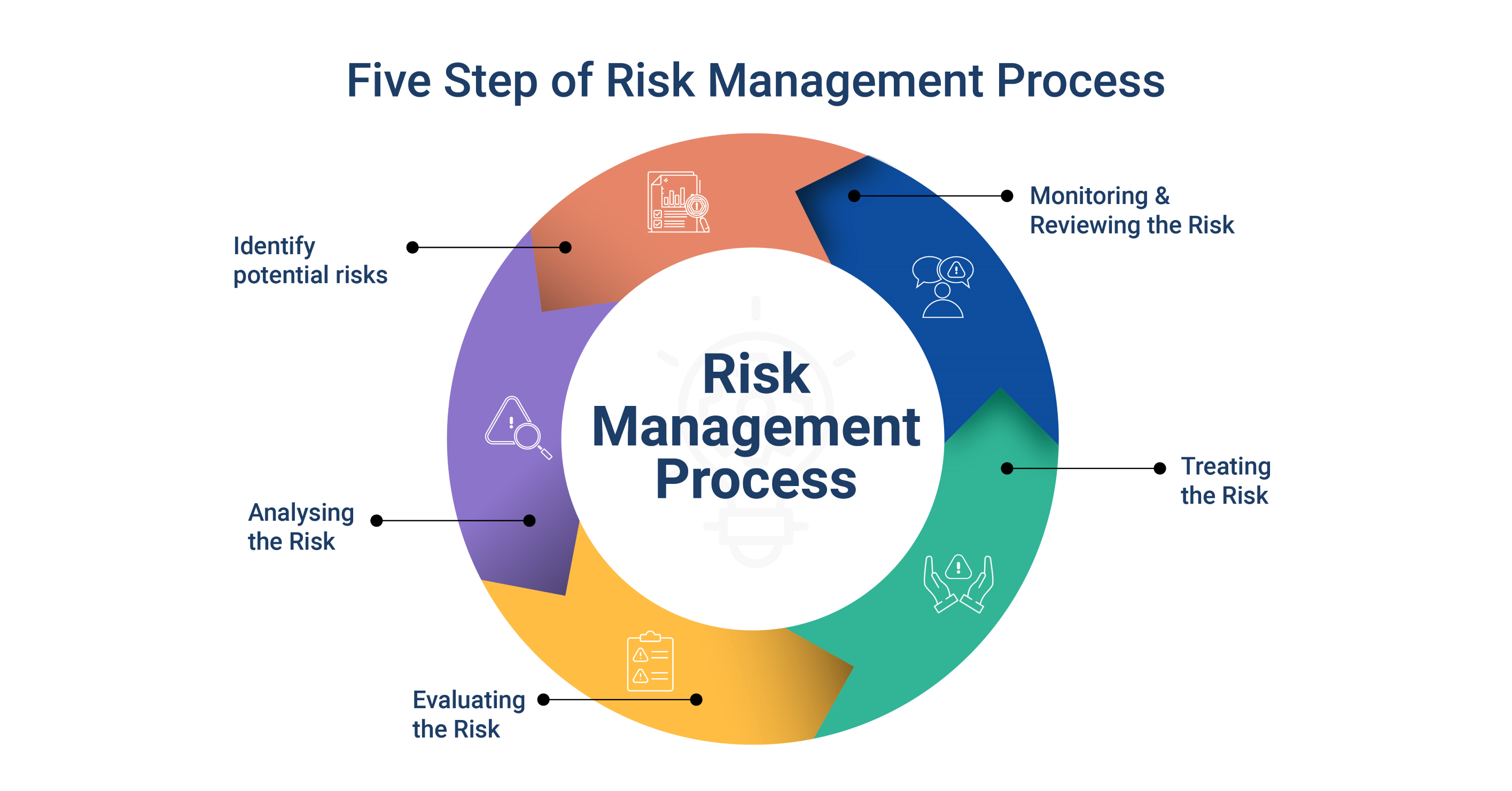
Five Steps of Risk Management Process
What is enterprise risk management software and why do you need it?
Enterprise risk management software is a specialized type of risk management software to help large-scale enterprises identify potential risks and weigh them against business opportunities.
- Strategic risk information is often held in disparate Excel spreadsheets making it difficult to identify, understand, and draw relationships between causes, consequences and their controls, and actions.
- It's often difficult to map and interpret interdependencies and commonalities, and any effort to create a risk map is entirely manual and prone to human error.
- Communicating this complex information or sharing it collaboratively, is difficult and time-consuming, especially when executives and key decision makers across the business only require the crucial messages and high-level insight.
“It's fair to say that before SharpCloud, it was really difficult to keep momentum on action tracking, progress updates, and closures. It has been transformational in showing information in this way to multiple risk control and action owners.”
Sue Nugent, Risk, BCM & Insurance Manager
Devon & Somerset Fire and Rescue
Benefits of enterprise risk management software
Enterprise risk management software makes it easier for businesses to collaboratively identify, assess and manage their risks, helping them to reach a shared understanding and make more informed decisions. Benefits include:
1) Standardized risk assessments
When multiple people perform risk assessments, inconsistencies can arise. ERM tools offer templates to standardize these assessments, ensuring all relevant information is included. This consistency makes it easier to identify risks and standardizes the overall risk management process.
2) Better compliance coordination
Potential risks are daunting for companies, but effective communication is key to preparation. Compliance managers utilize ERM tools to outline project compliance risks, create action plans, and assign tasks to mitigate them. This clarity ensures accountability and enables proactive identification and prevention of emerging risks, enhancing regulatory compliance.
3) Business continuity
ERM platforms typically include business continuity management, enabling risk managers to define key risk indicators and their corresponding mitigation strategies. Risk analytics provide actionable insights into the organization’s risk exposure, empowering risk owners to take timely actions. Moreover, logging risk mitigation activities in the ERM tool enhances corporate governance and establishes a transparent audit trail. This approach facilitates faster responses to similar risks in the future.
What risk management tool is best for you?
Maintaining business operations in an increasingly complex and unsettled environment requires proactive, integrated solutions across people, data, and infrastructure to ensure alignment when challenges arise. To minimize and manage risks, companies adopt risk management software that combines the following features:
- Risk Identification: Scans networks and identifies risks and vulnerabilities as they arise
- Risk Visualization: Transforms complex risk analysis data into compelling and easy to understand visuals
- Risk Assessment: Analysis of risks and vulnerabilities to determine how severe the threat is and what resources it would affect
- Risk Prioritization: Prioritize what risks will cause the most damage and alert operators to the appropriate task
- Centralized Dashboard: Monitoring risks and solutions with easy-to-understand visual reporting and dashboards
- Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring the company’s risk management processes meet all necessary regulatory compliance by defining and tracking processes and required compliances
- Issue management: Managing the execution of key risk-based projects and ensuring critical risk management issues are identified and accounted for
- Document management: collaborating and sharing documents and reports in real time
Top risk management tools
Let's take a look at some of the top solutions:
1) Riskonnect
Riskonnect is an integrated risk management leader with GRC solutions for project risk, internal audits, compliance, third-part, and enterprise risk management.
Riskonnect’s risk management platform integrates insurable and non-insurable risks for an actionable 360 view of the company’s risk profile. The workflow tool lets companies quickly assign actions and priorities to mitigate risk as it happens, while risk heatmaps give stakeholders a quick understanding of the most vulnerable parts of the business. Then use Riskonnect’s prebuilt and customizable reporting templates to communicate progress and increase awareness across the organization.
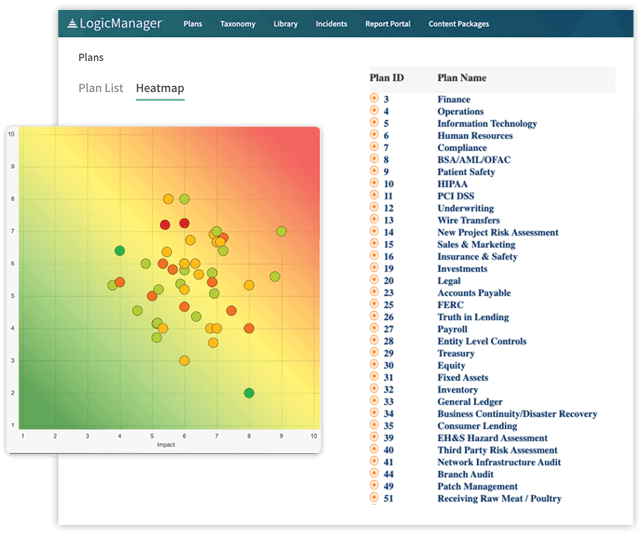
2) LogicManager
LogicManager’s ERM software helps simplify developing, improving, and reporting on your business risk program and enables better business decisions.
LogicManager uses a risk taxonomy structure to help companies categorize their risk across departments and business units to surface the most urgent vulnerabilities across an organization’s information silos. The taxonomy structure also allows risk and compliance teams to better allocate resources without duplication, providing the company with a faster, more organized response to risk environments.
3) LogicGate
LogicGate Enterprise Risk Management is an ERM solution that helps turn risk management into opportunity management by transforming your risk strategy from reactive to proactive.

LogicGate offers a full platform of modular no-code enterprise risk management solutions that companies can choose from to improve risk management as the company grows, including ERM, third-party, IT, compliance, and incident management solutions that work together in a single interface. Companies can use the pre-built workflows and drag-and-drop form builder to customize identification, notification, and response protocols.
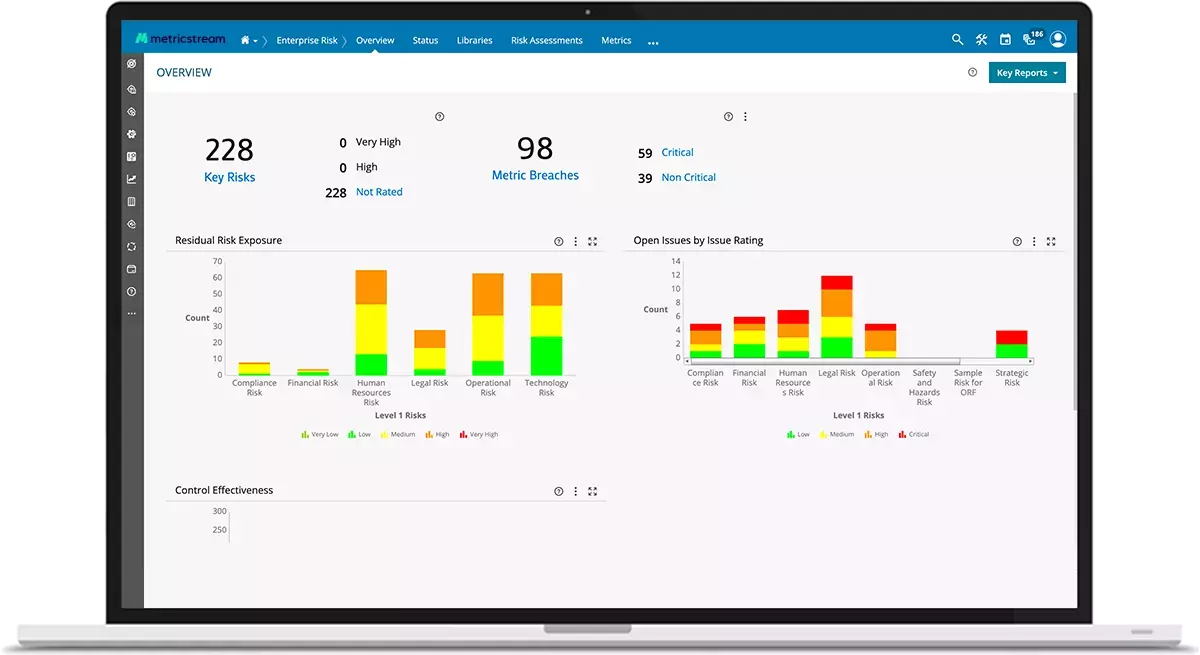
4) MetricStream
MetricStream’s ConnectedGRC is a governance, risk, and compliance platform for enterprise companies looking to increase their resilience after an incident. The tools combine traditional risk, compliance, and audit tools with cybersecurity and third-party controls to ensure a full-spectrum view of the enterprise’s risk profile. The collaborative platform increases transparency between otherwise-siloed departments, which contributes to higher agility in the face of risk.
MetricStream is easily configurable and allows companies to design reports for senior executives and board members.
5) SharpCloud
As a platform designed to enable more informed strategic decision making, SharpCloud transforms and connects your siloed data imported from Excel, SharePoint, and other line of business tools into compelling and easy to understand visuals.
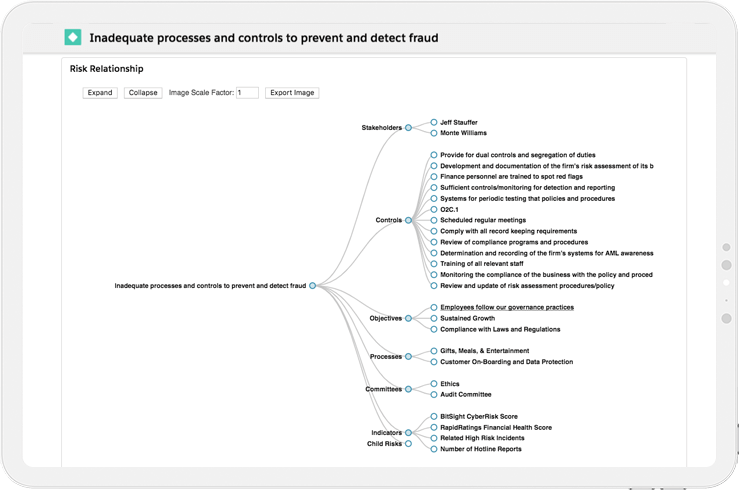
Using SharpCloud's risk BowTie template, you can create an interactive and visual story for each risk and gain a new perspective as spreadsheet rows and columns seamlessly transform into a familiar bow-tie format and other flexible data-rich views. Content is centralized, easy to view, edit, share, and understand.
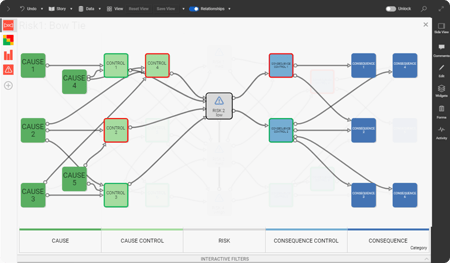
Clearly identified relationships help to understand how various risks interconnect with one another and the wider business, providing in-depth, practical insights - a key element that spreadsheets struggle to provide. Clear visual presentation and a variety of flexible views and interactive filters make it easier than ever before to proactively identify, assess and prioritize risk ahead of time - you can see exactly where your key decisions are.
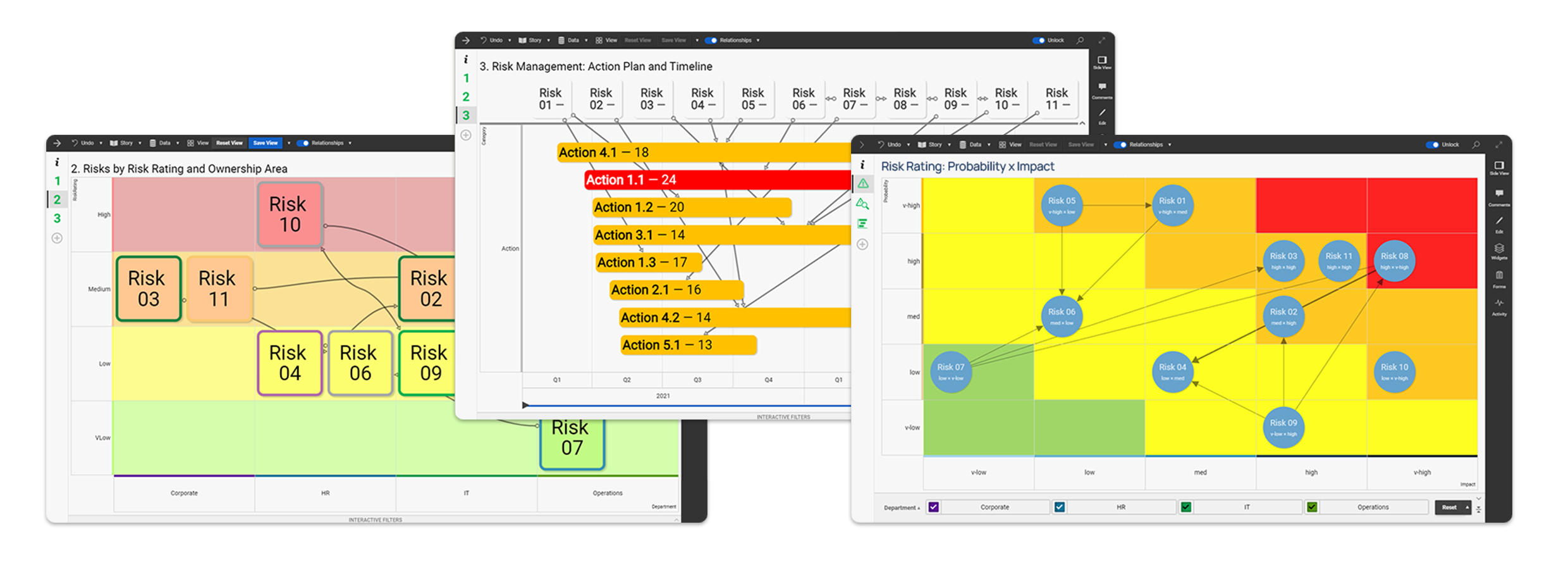
Data is automatically updated from individual spreadsheets into the relevant risk stories, ensuring that all data and content rolled up into the high level portfolio story, is real time and accurate for key stakeholders and board directors. Day to day processes, communication, and ultimately decision making, become more efficient and productive.
6) Sword - Active Risk Manager (ARM)
Active Risk Manager is a suite of enterprise risk management applications, deployed on-premise or hosted in the cloud, which enables medium to large businesses to identify, analyze and mitigate significant risks across the organization. Features include qualitative and quantitative risk assessments, performance management, heatmaps and more. Active Risk Manager’s risk performance manager tool helps businesses develop and share reports using in-built templates, facilitating strategic decision making and employee engagement.
It's ARM SNAPPit mobile incident management module allows users to report accidents across various projects and review controls, treatment plans, follow-up actions, providing insights into operations. Active Risk Manager facilitates integration with various third-party applications such as Oracle, SAP, Infor and Microsoft SharePoint.
7) CAMMS.Risk
Camms.Risk is a best-practice, cloud-based risk management solution that provides a comprehensive integrated approach to governance, risk and compliance and encompasses risk management, compliance management, incident reporting and monitoring, workplace health and safety, audit management, IT risk management as well as flexible registers and workflows.
Camms.Risk allows for an integrated approach linked to the unique strategies or corporate plans associated your organization. It has an intuitive, highly visual dashboard-based UI to make authorized user access less clunky and comes with pre-configured risk management templates. These can then be customized to make identification, tracking, action assignment, approval, and case-wide monitoring closely aligned to the existing business strategy.
8) Diligent
Diligent Compliance is a risk management solution designed to help organizations maintain regulatory compliance across internal and external processes to improve business continuity. Professionals can upload relevant corporate policies to the platform and create reports for auditors, regulators, and leaders.
Using Diligent Compliance's dashboards and reports, administrators can analyze compliance requirements, identify issues or discrepancies and build suitable remediation strategies. Administrators can leverage best practice frameworks and standards to measure the efficiency of ongoing compliance programs in accordance with organizational, jurisdictional, and industry regulations.
Additionally, supervisors can allocate tasks to specific team members or departments and configure access permissions for the staff. Diligent Compliance enables enterprises to streamline audit processes and backup critical information for future reference.
Choosing the best ERM solution
Enterprise risk management is critical for businesses that must abide by federal and international regulations, especially those in financial services, insurance, and healthcare industries.
All companies increasingly rely on technology to manage day-to-day operations, and enterprise risk management software holds a critical position in IT infrastructure. The best risk management platforms use risk data to identify and assess dependency risks that could derail a planned project or essential business functions.
ERM software keeps businesses operating as safely and successfully as possible. Identify key risks to your business objectives and prevent or prepare for them with risk management processes established by an enterprise risk management system.
FAQ's
Here’s a quick summary of the differences:
1. Scope
Risk Management: Focuses on specific areas or departments within an organization.
ERM: Takes a holistic view, covering the entire organization.
2. Approach
Risk Management: Uses a siloed approach, addressing risks independently within departments.
ERM: Utilizes an integrated approach, considering interdependencies and aligning with overall objectives.
3. Integration
Risk Management: Operates as a standalone function within departments.
ERM: Embeds risk management into the organization's culture and decision-making processes.
4. Objectives
Risk Management: Aims to minimize losses within specific areas.
ERM: Seeks to create and protect enterprise value, supporting long-term strategic goals.
5. Coordination and Communication
Risk Management: Risk information may be isolated, leading to gaps or overlaps.
ERM: Promotes transparent communication and coordinated efforts across the organization.
6. Leadership and Oversight
Risk Management: Managed at the departmental level with limited senior oversight.
ERM: Involves senior leadership and board of directors, ensuring alignment with strategy and accountability.
Enterprise Risk Management (ERM) addresses a wide variety of risks that can impact an organization. These include:
-
Operational Risks: Risks arising from day-to-day business operations, such as system failures, process inefficiencies, or supply chain disruptions.
-
Financial Risks: Risks related to the financial health of the organization, including market fluctuations, credit risk, liquidity issues, and investment losses.
-
Strategic Risks: Risks that could affect the achievement of the organization’s strategic goals, such as changes in the competitive landscape, shifts in customer preferences, or ineffective business strategies.
-
Compliance Risks: Risks associated with failing to comply with laws, regulations, and industry standards, which can result in legal penalties and reputational damage.
-
Reputational Risks: Risks that could harm the organization's reputation, such as negative publicity, social media backlash, or unethical behavior.
-
Security Risks: Risks related to the protection of the organization’s assets, including cybersecurity threats, data breaches, and physical security breaches.
-
Environmental Risks: Risks stemming from environmental factors, such as natural disasters, climate change, and resource scarcity.
-
Legal Risks: Risks arising from legal actions or disputes, including lawsuits, intellectual property issues, and contractual obligations.
-
Technological Risks: Risks associated with technology, including system obsolescence, technological innovation, and IT infrastructure failures.
-
Human Resources Risks: Risks related to the organization’s workforce, such as talent shortages, labor disputes, and employee misconduct.
-
Political Risks: Risks arising from political changes, such as regulatory shifts, government instability, and changes in trade policies.
By addressing these and other risks comprehensively, ERM helps organizations safeguard their assets, achieve their objectives, and maintain their competitive edge.
The eight components of Enterprise Risk Management (ERM), as outlined in the COSO (Committee of Sponsoring Organizations of the Treadway Commission) framework, are:
-
Internal Environment: The internal environment sets the tone of an organization and influences the risk consciousness of its people. It includes the organization’s risk management philosophy, risk appetite, integrity, ethical values, and the environment in which they operate.
-
Objective Setting: Objectives must exist before management can identify potential events affecting their achievement. ERM ensures that management has a process in place to set objectives and that these objectives align with the organization’s mission and are consistent with its risk appetite.
-
Event Identification: Internal and external events that could affect the achievement of an organization’s objectives must be identified. ERM distinguishes between risks (which have a negative impact) and opportunities (which have a positive impact) and ensures they are effectively managed.
-
Risk Assessment: Risks are analyzed, considering likelihood and impact, as a basis for determining how they should be managed. Risks are assessed on an inherent and a residual basis, ensuring a thorough understanding of the potential consequences.
-
Risk Response: Management selects risk responses—avoidance, reduction, sharing, and acceptance—based on the organization’s risk appetite and cost-benefit considerations. These responses help align risks with the organization’s risk tolerance and risk appetite.
-
Control Activities: Policies and procedures are established and implemented to help ensure that risk responses are effectively carried out. These activities occur throughout the organization, at all levels and in all functions.
-
Information and Communication: Relevant information must be identified, captured, and communicated in a form and timeframe that enable people to carry out their responsibilities. Effective communication also flows down, across, and up the organization.
-
Monitoring: The entire ERM process must be monitored, and modifications should be made as necessary. Monitoring is accomplished through ongoing management activities and separate evaluations, ensuring that ERM remains effective over time.
These components work together to provide a robust framework for identifying, assessing, managing, and monitoring risks across the organization.
- Improved decision-making: By providing a comprehensive view of risks, ERM helps management make informed decisions that balance risk and reward.
- Enhanced performance: ERM supports the achievement of strategic objectives by managing risks that could hinder performance.
- Increased resilience: ERM helps organizations better withstand shocks and disruptions by anticipating potential risks and developing contingency plans.
- Regulatory compliance: ERM helps ensure that the organization complies with relevant laws and regulations, reducing the risk of legal penalties and reputational damage.
- Stakeholder confidence: Effective ERM practices can enhance the confidence of stakeholders, including investors, customers, and employees, in the organization’s ability to manage risks.